CS231n Lecture2 정리
Lecture2 : Image Classification pipeline
Image Classifier의 기본적인 구조, 그리고 가장 간단한 kNN (K-Nearest Neighbors) 에 대하여 설명한다.
Image Classifier
Input: 이미지, Output: 그 이미지의 label (분류)1
2
3def classify_image(image):
# codes
return class_label
Train, Predict의 큰 틀을 가짐
Nearest Neighbor
Train: 저장만 함
Predict: 가장 유사한(거리가 가까운) 이미지의 label을 출력
K-Nearest Neighbors
가장 가까운 근처 K개의 점 중 다수의 label을 선정
outlier들을 배제할 수 있다.
Distance Metric
L1(Manhattan) distance
- $d_1(I_1, I_2) = \sum_{p} |I_1^p-I_2^p|$
- 같은 거리의 점들이 마름모 형태
L2(Euclidean) distance
- $d_2(I_1, I_2) = \sqrt{\sum_{p}(I_1^p-I_2^p)^2}$
- 같은 거리의 점들이 원 형태
Hyperparameters
- 정의: Train 되지 않고 내가 직접 정하는 parameters (set rather than learn)
- 대부분 problem-dependent 하여, 직접 다 돌려보고 선택하는 경우가 많음.
Setting Hyperparameters
- IDEA: Data를 train, val, test로 랜덤하게 나누어, train에서 모델 학습, val에서 hyperparameter 설정, test에서 최종 검정을 한다.
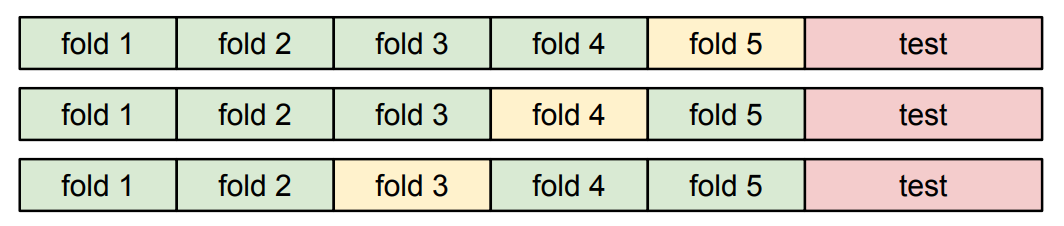
- Cross-Validation: data를 여러 fold 들로 나누어, 각 fold를 validation으로 사용해 보고 결과를 평균낸다. Small Dataset들에선 유리하지만, 딥러닝은 보통 그렇지 않으므로 자주 쓰이지는 않음.
CS231n Lecture2 정리
http://yxxshin.github.io/2022/07/10/2022-07-10-CS231n-Lecture2/





